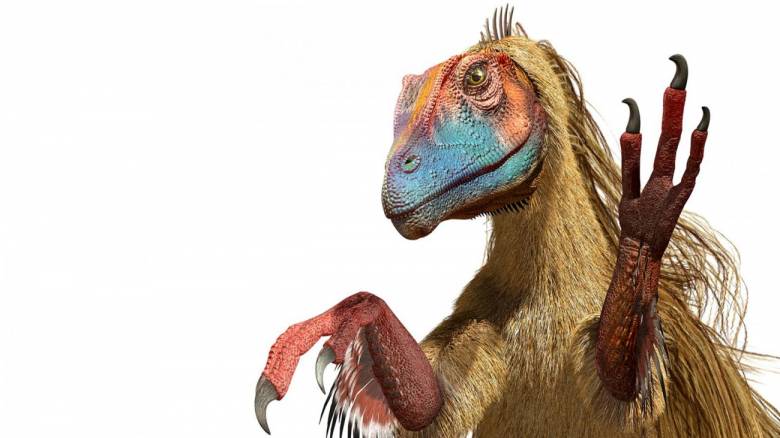Кто такой stegosaurus rex
Сравнение всех динозавров из Мира и Парка Юрского периода
Давайте сегодня поговорим об огромных древних рептилиях, к сожалению, на данный момент полностью вымерших. Кстати, в реальном мире, используя гены птиц, близких родственников динозавров, сейчас пытаются вернуть их жизни. Так что гигантские ящеры с наших экранов очень скоро шагнут в этот мир. А пока мы посмотрим на самых крутых и интересных созданий из Мира и Парка Юрского периода, причем сравнивать будем клонов, созданных учеными из фильмов, так как в реальности у животных были габариты поскромнее.
А это видео версия обзора. В ней в качестве бонуса послушаем мощный рёв гигантских доисторических ящеров.
Рост: 0,6 метра / Длина: 1 метр / Вес: 3 кг
Небольшой двуногий теропод. Длинная узкая голова животного посажена на длинную изогнутую шею. Череп и нижняя челюсть тонкие и изящные, а значит, довольно хрупкие. В челюстях маленькие и острые зубы. Шея довольно подвижная и позволяет ловко вращать голову во все стороны, что помогает ему хватать добычу. У компсогната длинные задние конечности и ещё более длинный хвост, который он использует для балансирования во время движения. На передних конечностях по три пальца с острыми когтями, ими он хватает добычу. Тонкий череп узкий и длинный, оканчивается клиновидной мордой. Тело компсогната покрыто перьями.
Рост: 1,6 метра / Длина: 3,6 метра / Вес: 140 кг
Рост: 1,7 метра / Длина: 3,9 метров / Вес: 150 кг
Рост: 1,7 метра / Длина: 9,6 метров / Вес: 6 тонн
Рост: 2,6 метра / Длина: 9,3 метров / Вес: 2,1 тонны
Рост: 2,9 метров / Длина: 10,4 метра / Вес: 1,6 тонн
Плотоядный Южно-американский плотоядный динозавр позднего Мелового периода. Тело Карнотавра покрыто прочной броней, состоящей из отдельных щитков как у современных крокодилов. По всей длине спины карнотавра идут шипы, как у современной игуаны. Череп украшают рога, использующиеся для привлечения самок и сражений. Слабость челюстей компенсируется очень развитыми задними конечностями, динозавр развивает скорость в 48-56 км/ч. У карнотавра сильная шея, которую он использует на охоте с головой, работая как топор, продолжая кусать и бить ей добычу, пока та не умрёт. Они выбирают среднюю или маленькую добычу, вроде небольших динозавров или детёнышей. В охоте или драке карнотавры полагаются на свои когти на задних лапах и мощные челюсти.
Рост: 3 метра / Длина: 5,4 метров / Вес: 120 кг
Род птерозавров, живший в позднем меловом периоде на территории современной Северной Америки. Он умеет летать, благодаря огромным крыльям и лёгким полым костям. Размах крыла птеранодона достигает 9 метров. У птеранодона маленький негнущийся хвост. У него длинный вытянутый беззубый клюв, который сужается и становится острее на кончике. Благодаря нему, птеранодон может с лёгкостью вытащить рыбу из воды. На затылке у него длинный гребень, для привлечения самок. Птеранодоны массово заселяются на каменистых скалах у морей, с восходящими потоками, помогающие ящерам взлететь. Общаются птеранодоны, с помощью резких визгов и криков, как современные чайки. В кино они обладают огромной силой, благодаря которой могут поднимать тяжёлый груз вроде взрослого человека, правда не долго.
Рост: 3,1 метра / Длина: 7,3 метра / Вес: 1 тонна
Легендарные динозавры выглядят совсем не так, как мы привыкли считать
Знаменитые монстры вроде тираннозавров и велоцирапторов, вероятнее всего, не похожи на монстров из нашего воображения и уж точно вели себя по-другому. У многих из нас в детском возрасте, и я говорю за себя абсолютно искренне, был тяжелый период любви к динозаврам.
И вот теперь выясняется, что многое из того, что я знал, было неправдой. Оказывается, современный научный взгляд на эти вещи на шаг обходит популярный образ динозавров.
До «возрождения динозавров» конца 60-х годов динозавры всегда изображались как вялые и жвачные. Но эксперты поняли, что динозавры вели активный образ жизни и постепенно довели это до широкой публики — в том числе и с помощью «Парка Юрского периода» 1993 года.
За последние два десятилетия мы стали свидетелями еще одной крупной революции в наших представлениях о динозаврах, благодаря новым окаменелостям из Китая и достижениям в области технологий. Но большинство этих выводов никак не повлияли на расхожее представление о динозаврах.
И сейчас я понимаю, как сильно образы легендарных динозавров въелись в мою память — с детства. Это как считать Плутон планетой Солнечной системы.
Но теперь вы можете и не узнать этих динозавров.
Велоцираптор
Давайте начнем с идеи, о которой многие слышали, но немногие приняли: у некоторых динозавров были перья. Не просто пару перышков тут и там, а полностью покрытое перьями тело.
Уже в 1980-е годы некоторые палеонтологи начали подозревать, что динозавры-то пернатые, оказывается, твари. Все чаще находили окаменелости примитивных дромеозаврид — семейства, к которому принадлежит велоцираптор (Velociraptor) — с полностью оперенными крыльями. Тем не менее живописания этого культового хищника оставались довольно традиционными.
Все изменилось в 2007 году, когда американские ученые обнаружили бугорки для перьев на кости предплечья ископаемого велоцираптора. Эти бугорки находятся там, где крепится перо, и предоставляют убедительные доказательства в пользу пернатых и похожих на птиц велоцирапторов.
Те динозавры размером с человека, которых показывали в «Парке Юрского периода», не имели ничего общего со своими настоящими предками.
«Если бы животные вроде велоцираптора были живы сегодня, мы сразу бы решили, что они похожи на необычных птиц», — говорит Марк Норелл из Американского музея естественной истории. И это отражается не только в перьях: настоящие велоцирапторы были размером с индюшек.
Майкл Крайтон, автор оригинального романа «Парк Юрского периода», создавал своих «рапторов» по образу более крупных дейнонихов (Deinonychus). И, по всей видимости, намеренно назвал их неправильно, поскольку ему показалось, что «велоцираптор» звучит более драматично.
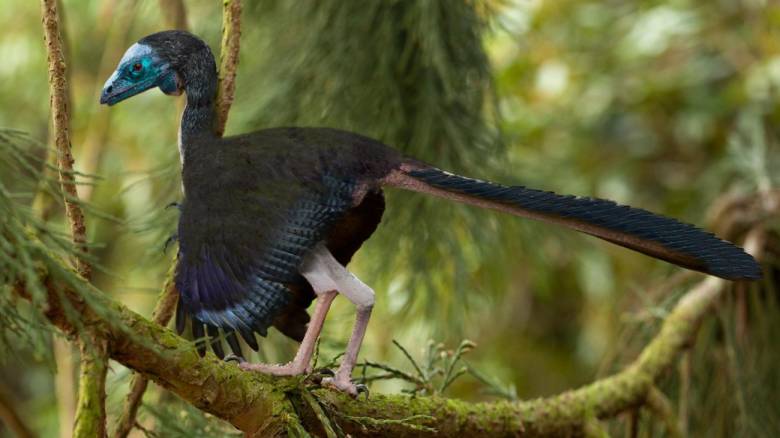
Археоптерикс
Археоптерикс широко считается «пропавшим звеном» между динозаврами и птицами. Этот загадочный статус привлек к ним очень много внимания, и не только положительного.
Обвинения в подделке преследуют окаменелости археоптериксов много лет, как правило, от людей, которым не нравится настолько четкое доказательство эволюции.
На самом деле, новые исследования показывают, что археоптериксы могут и не быть пропавшим звеном, но явно не по причинам, продвигаемым противниками эволюции. После открытия очень похожего на археоптерикса динозавра в Китае, ученые предположили, что знаменитый птичий предок мог на самом деле предшествовать небольшим хищным динозаврам вроде велоцирапторов. С тех пор эта версия оспаривается.
Даже если считать археоптерикса первой птицей, этот ярлык не соответствует действительности. «Принципиально невозможно провести черту на эволюционном дереве между динозаврами и птицами», говорит Стив Брусатте из Университета Эдинбурга в Великобритании, соавтор работы 2014 года, исследующий эволюцию первых птиц.
Все указывает на то, что не было никакого недостающего звена между птицами и динозаврами, а только постепенный переход с участием множества пернатых промежуточных видов.
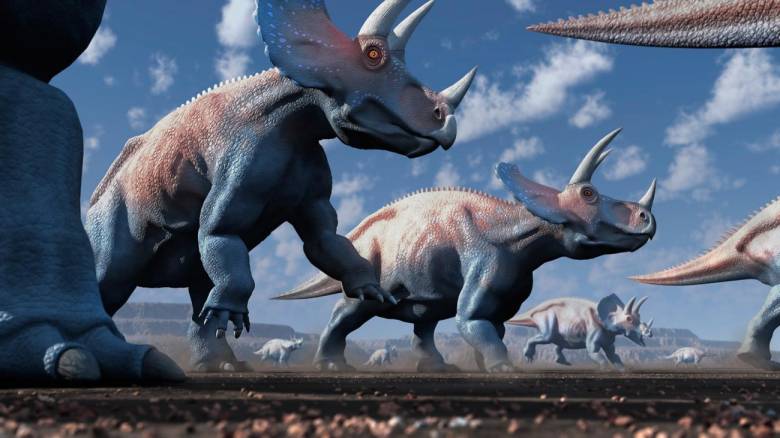
Трицератопс
Этот вечный противник тираннозавра и излюбленная модель для пластиковых фигурок — кто не любит трицератопса?
Поэтому когда в 2009 году Джон Сканнелла и Джон Хорнер опубликовали работу, в которой предположили, что трицератопс был просто ювенильной версией более крупного, но менее известного торозавра (Torosaurus), на них обрушились волны ненависти, а после пришло разочарование. Был изобретен хэштег #TriceraFAIL. Люди решили, что их любимого динозавра просто выдумали.
Но все было не так. Очень скоро комментаторы стали указывать на то, что трицератопсов нашли раньше, так что если и стоит кого убирать, то это торозавров. Но урок оказался очень важным. Наши знания о динозаврах зачастую основаны на скудных окаменелостях, так что даже известные виды претерпевают изменения.
Бронтозавр
Бронтозавр получил свое имя в честь архетипических зауропод: огромных, неуклюжих травоядных с длинными шеями. Но в течение сотни лет ученые были уверены, что этот динозавр никогда не существовал.
Скелет, который впервые был представлен как бронтозавр, остался от апатозавра с черепом камарозавра.
Однако в 2015 году группа ученых представила анализ, демонстрирующий существенные различия между оригинальным бронтозавром и ископаемым апатозавром, предполагая, что род бронтозавров должен быть воскрешен.
Ключевой отличительный фактор, говорит команда, это размер. В семье гигантских рептилий апатозавр был огроменным.
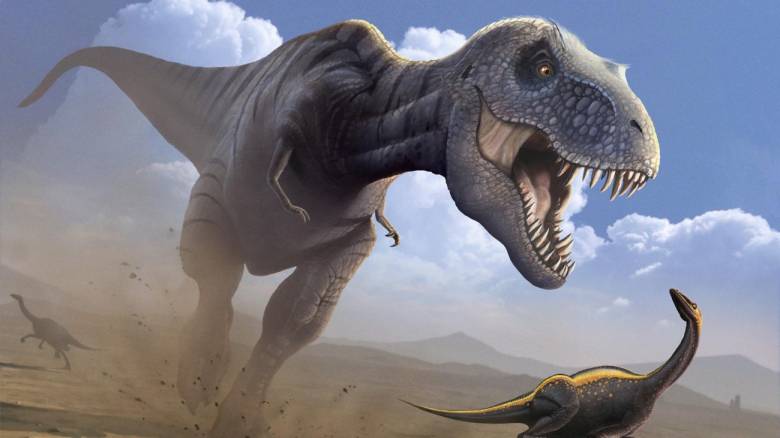
Tyrannosaurus rex
Некоторые ученые определенно выгораживали тираннозавра. После десятилетий оправданий, мол, что это был смиренный поедатель травы, а не свирепый хищник из популярного представления, теперь эта ящерица переживает очередной кризис идентичности.
По мере того, как пернатая революция охватывала палеонтологию, эксперты начали задумываться и над родом Tyrannosaurus. Конечно, разве мог самый харизматичный хищник всех времен быть пернатым?
Ни грамма оперения не было обнаружено в свыше 50 останков T. rex по всей Северной Америке. Но вместе с раскопками в Китае потянулись очень и очень интересные намеки.
В 2004 году нашли примитивного тираннозавроида с покрытием из перьев, подобных тем, которые были у других небольших хищных динозавров. За этим последовало открытие Yutyrannus в 2012 году — что означает «пернатый тиран». Этот гигантский хищник был в тесном родстве с T. rex, и не только по части размеров. Он был покрыт длинными перьями.
Эти данные свидетельствуют о том, что на самого известного хищника всех времен нужно взглянуть по-другому. Вопрос в том, был ли пернатый тираннозавр не таким страшным, как ревущий и пожирающий юристов монстр, которого мы все так любим?
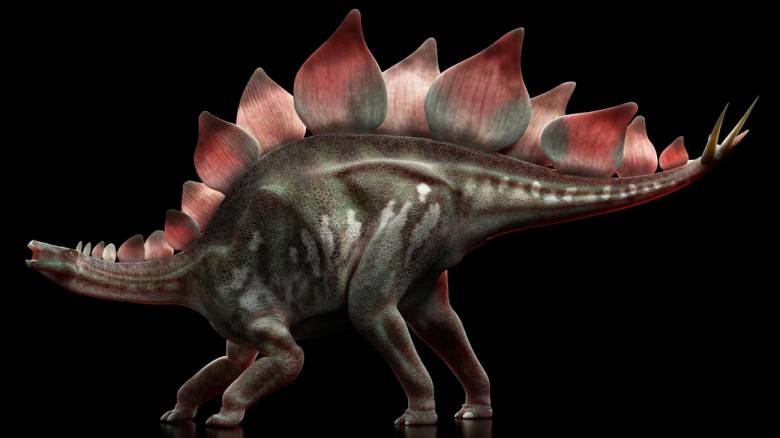
Стегозавр
Эксперты славятся своим умением придумывать дурацкие объяснения странным особенностям динозавров; объяснения, которые уверенно заползают в популярные мнения и остаются там.
К примеру, широко распространен «факт» о том, что у стегозавра был дополнительный мозг в области малого таза, который компенсировал крошечный мозг (мозжечок?) в маленькой голове.
Но нет, стегозавр, может, и не был самым остроумным среди своих друзей, но в дополнительном мозге не нуждался. Эта дополнительная полость, которая породила миф, вероятнее всего, размещала «гликогеновое тело»: структуру, которая есть у многих птиц и которая участвует в хранении энергии.
А еще у него есть пластины на спине.
В течение некоторого времени самой популярной теорией было то, что самая отличительная черта стегозавра представляет собой… «солнечные панели», помогающие ему регулировать температуру тела. Но это всегда оставалось предметом бурных научных баталий. Если уж это действительно так, почему другие украшения стегозавров больше похожи на шипы, чем на панели?
Разнообразие шипов стегозавра сыграло роль в другом ходе мыслей. Подобно яркому и пестрому оперению тропических птиц, эти пластины, возможно, помогали динозаврам отличать друг друга и привлекать партнеров.
Секс мог быть ключевым фактором развития множества экстравагантных черт, наблюдаемых у динозавров. За последние годы все, начиная длинными шеями зауропод и заканчивая пышным жабо цератопсов, стали причислять к половому отбору.
Пахицефалозавр
И хоть этот динозавр не входит в первый класс легендарных ящеров, пахицефалозавр хорошо известен среди поклонников динозавров своей бронированной головой.
Этих динозавров почти эксклюзивно изображали участвующими в битвах, сталкивающимися своими головами. Пахицефалозавры имели куполообразные головы с мощным армированным черепом. Считалось, что самцы использовали эти встроенные тараны, чтобы бороться друг с другом, подобно баранам наших дней.
Однако некоторые ученые усомнились в том, что пахицефалозавры были драчунами.
«Наши исследования показали, что пахицефалозавры могли приложиться головами лишь раз и последующая травма могла бы их убить», говорит Джон Хорнер из Университета штата Монтана в США, который изучал микроструктуру черепных тканей динозавров.
Он предполагает, что купола были очередным способом привлечь партнеров (половых, естественно, а не по бизнесу).
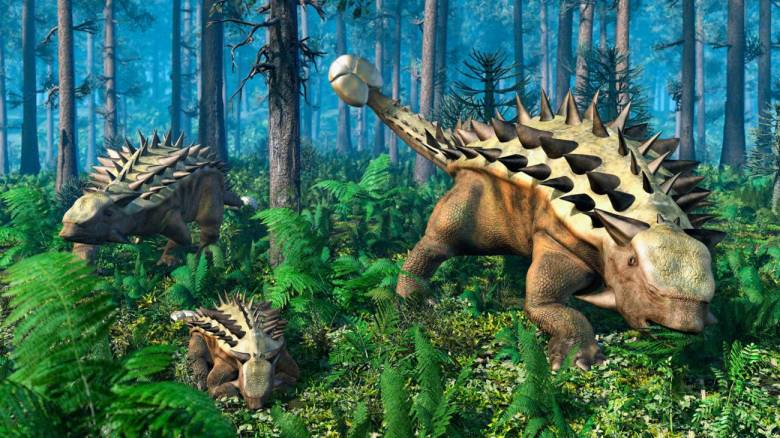
Анкилозавр
Покрытый толстыми броневыми пластинами от головы до хвоста, анкилозавр был таким средневековым рыцарем мелового периода.
Современные палеонтологи используют новейшие технологии, чтобы выжать все больше и больше информации из окаменелостей. В 2004 году Торстен Шейер из Университета Бонна в Германии использовал поляризационную микроскопию, чтобы раскрыть новые замечательные уровни сложности панциря анкилозавров.
Выяснилось, что громоздкая на вид броня обладает сложной микроструктурой из костей и коллагена, аналогичной структуре стекловолокна или кевлара.
«Такой панцирь был очень прочным во всех местах, — говорит Шейер. И на удивление легким. — Современные композитные материалы, которые используются для создания лопастей ветряных ферм или бронежилетов, основаны на том же принципе».
Похоже, анкилозавр был больше похож на современного суперсолдата, чем на средневекового рыцаря.
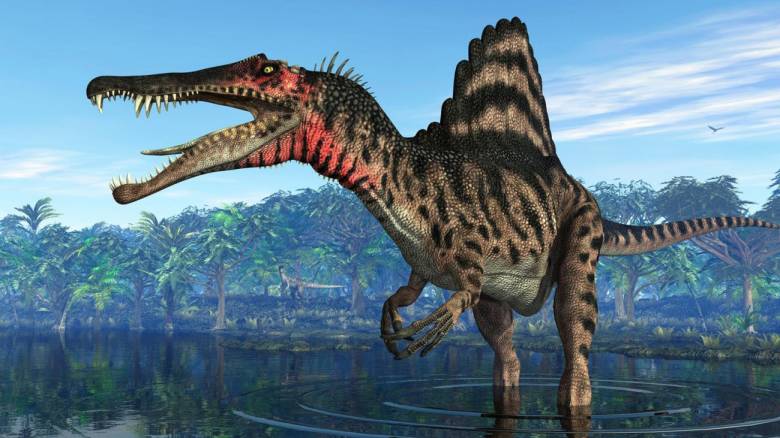
Спинозавр
Еще один динозавр, который стал знаменит благодаря фильму «Парк Юрского периода», это спинозавр: в фильме он сразился с тираннозавром.
Легко понять, почему выбор киношников пал на спинозавра. Будучи 15,2 метра длиной, он на 2,7 метра длиннее тираннозавра. У него также была длинная и страшная челюсть и причудливый «парус», торчащий из спины.
Спинозавр всегда был загадочным динозавром, известным лишь по фрагментам скелета, обнаруженного в пустынях Северной Африки. Но в 2014 году группа археологов во главе с Низаром Ибрагимом из Университета Чикаго в Иллинойсе заявила об обнаружении новых останков. Эти окаменелости, похоже, подтвердили то, что давно подозревалось: спинозавр является единственным водоплавающим динозавром.
Анализ Ибрагима выявил существо с маленькими задними конечностями, которые больше подходят для плавания, чем для охоты на суше. У него также было длинное крокодилье рыло и костная микроструктура, подобная микроструктуре костей других водоплавающих позвоночных.
«Работа над этим животным была похожа на изучение инопланетянина из космоса, — говорит Ибрагим. — Этот динозавр не похож ни на какого другого».
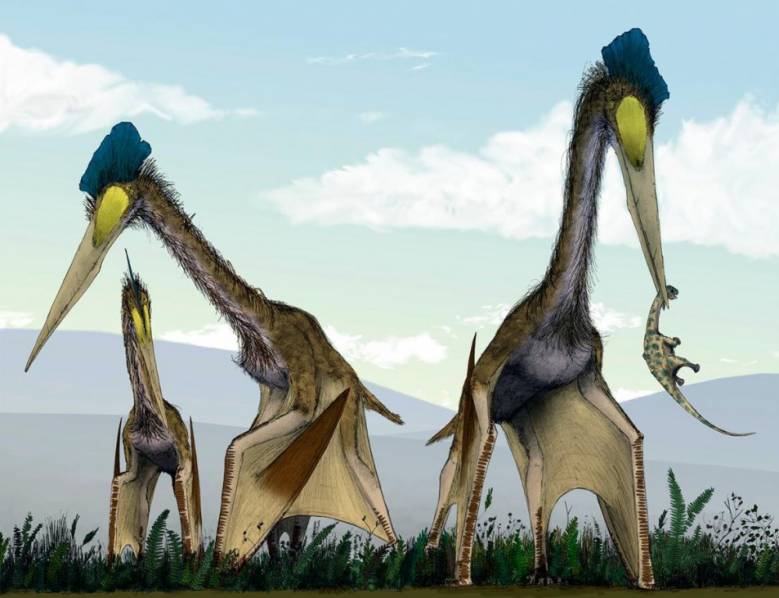
Бонус: птерозавры
Этот пункт не совсем считается, поскольку птерозавры не были динозаврами: факт, который периодически упускают из вида.
Многие из нас знакомы с названием «птеродактиль». Но под этим названием скрывается много групп летающих рептилий, которые коллективно называются «птерозаврами». И эта группа была просто огромной.
На одном конце спектра мы находим немиколоптеруса, крошечного птерозавра с размахом крыльев в 25 сантиметров (10 дюймов). Есть и твари покрупнее: аждархиды. Когда они расправляли крылья, их размах был колоссальных 10 метров. Если так судить, они были крупнейшими летающими животными всех времен.
Stegosaurus Rex Nowhere To Run Slowed Bass Boost
Загрузил: E X T C M U S I C 精英
Длительность: 6 мин и 5 сек
Your Gonna Kill You Spoiler Alert Random Squid Game Edit
You Re Really Joking At A Time Like This
We Fell In Love In October Pmv
Stegosaurus Nowhere To Run 8D Audio Use Headphone
Sueco Paralyzed Bass Boost
E X T C M U S I C 精英
Hayloft By Mother Mother Slowed Reverb
Elyotto Sugarcrash Lyrics
Stegosaurus Rex Nowhere To Run Slowed Deeper Version
Kayla The Awesome Song Editor
Lil Nas X Montero Call Me By Your Name Lyrics
Sub Urban Cradles Lyrics
Nowhere To Run But It S Only You Re Gonna Die I M Gonna Kill You Slowed
Your Gonna Die I M Gonna Kill You Edit
Nowhere To Run Stegosaurus Rex Lyrics
Stegosaurus Rex Некуда Бежать Замедленно Nowhere To Run Slowed Рус Саб Rus Sub
Doja Cat Get Into It Yuh Bass Boost
E X T C M U S I C 精英
Nowhere To Run That S Right I Win Tiktok Remix Slowed
Freddie Dredd Opaul Lyrics
Терма Шух Узбекча 2021
Civilization 6 Ost Kalinka
Siqilib Ichdim Biroz Mp3
What S My Name Nightcore
Худо Хофиз Ёри Чанд Солаи Ман
Snoop Dogg Wiz Khalifa 50 Cent Regulate Ft Pop Smoke
Farhod Saidow Kizmi Bu
Куйган Дилим Вайронгинам Мрз
Psy Oppa Gangnam Style
Last Day On Earth Survival Soundtrack
Gaullin Moonlight Slowed By Hunx
O Behold Kevin Morby
Alip Ba Ta Numb By Linkin Park Cover Reaction Omg This Was Fiyahhh
Обычаи И Традиции Прот Андрей Ткачёв 12 11 2016Г
Даю Акк Обожаю Вас Мои Лисята В Описание
Rebutan Anak Burok Ady Muda Live Limbangan Kersana Brebes Minggu 19 September 2021
Wizkid Blessed Video Ft Damian Marley
Народный Театр Общение Онлайн Читакль Читаем Стихи Есенина
22 De Octubre De 2021
Stegosaurus Rex Nowhere To Run Slowed Bass Boost
Praveen Tej A Lovely Long Drive With Ananya Scenes Mundina Nildana New Kannada Movie 2020
Complex Numbers Part 5 Airforce Navy X Group C M Parashar The Tutors Academy
Самые Топовые Новинки
Easter Tour 2020 Spring Home Decor Primitive Country
Fnaf Sfm Sister Location Mega Mashup Collab Part For Nightmare Molten
The Serenity Resort Shah Allah Ditta Islamabad
Kissing Strangers Meme Gacha Life
Мотопоход 1 К Сл По Алтайскому Краю
Musha Dariya Missing Target Latest Nuraalejo Comedy
I Love Animals Anduena
Saratkd Tiktok Shorts Tiktok Balkan Sara Tkd
Ihuriro Comedy Iyo Ugiye Kugura Agakingirizo Ukahasanga Umukobwa
Stegosaurus
| Царство: | Животные |
| Тип: | Хордовые |
| Класс: | Пресмыкающиеся |
| Надотряд: | Динозавры |
| Отряд: | Птицетазовые |
| Подотряд: | Thyreophora |
| Инфраотряд: | Stegosauria |
| Семейство: | Стегозавровые |
| Род: | Стегозавр |
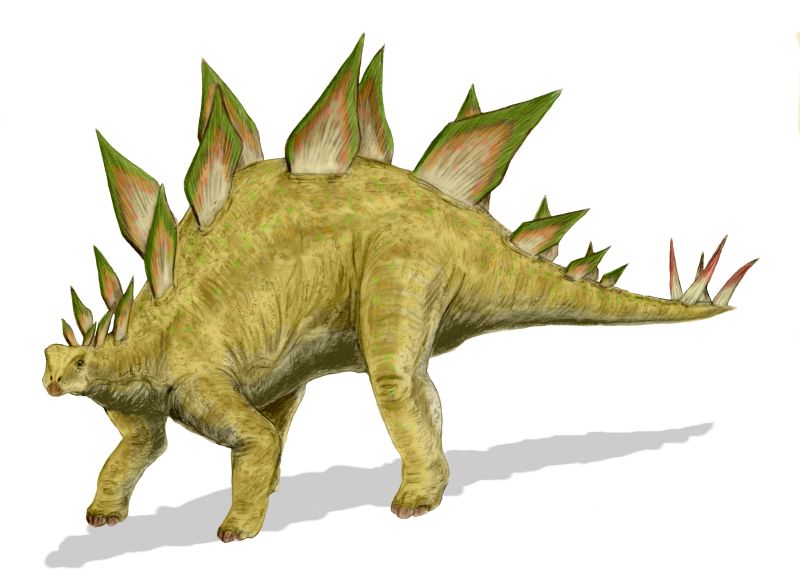
Стегозавры (лат. Stegosaurus ) — род позднеюрских травоядных динозавров, существовавший 155-145 млн. лет назад. В его составе выделено три вида. Благодаря шипам на хвосте и костяным пластинам на спине являются одними из самых узнаваемых динозавров.
Содержание
Открытие и изучение
Ископаемые останки стегозавра (Stegosaurus armatus) были обнаружены Г. Маршем в 1877 к северу от городка Моррисон, в штате Колорадо. Название было составлено Маршем из греческих слов στέγος (крыша) и σαῦρος (ящер), поскольку палеонтолог посчитал, что пластины лежали на спине динозавра и образовывали подобие двускатной крыши. Поначалу было описано множество видов стегозавров, которые впоследствии были объединены в три.
Описание
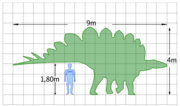
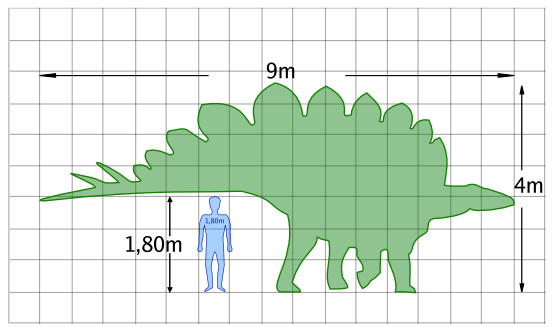
Стегозавры были крупнейшими представителями своего инфраотряда, включавшего также рода Kentrosaurus и Huayangosaurus. Их средняя длина составляла 9 метров (S. armatus), высота — 4 метра. Мозг динозавра был не больше чем у собаки: при весе животного около 4,5 тонн, его мозг весил лишь 80 грамм.
«Второй мозг»
Пластины
На спине стегозавра находились 17 костяных пластин, которые не были выростами каких-либо костей внутреннего скелета, а располагались обособленно. Некоторые палеонтологи, например, Роберт Беккер, полагают что пластины были подвижны и могли менять угол наклона. Крупнейшие пластины имели размеры 60×60 см. Их расположение долго было предметом спора, лишь в настоящее время научное сообщество пришло к консенсусу, что пластины образовывали два ряда на спине животного, при этом пластины одного ряда росли напротив промежутков в другом ряду.
Питание
Тем не менее, стегозавры были весьма успешным и распространённым родом. Палеонтологи предполагают, что они могли заглатывать камни, которые в желудке перемалывали пищу, как сейчас поступают многие птицы и крокодилы.
Также есть две гипотезы относительно того, с какой высоты стегозавр добывал пищу. Он либо оставаясь на 4 ногах объедал растущие на высоте около 1 метра листья, либо вставал на задние лапы и тогда достигал высоты до 6 метров.
Dinosaur Wiki
This wiki’s URL has been migrated to the primary fandom.com domain.Read more here
Stegosaurus
9 metres (30 ) feet long
At least three species have been identified in the upper Morrison Formation and are known from the remains of about 80 individuals. They lived some 150 to 145 million years ago, in an environment and time dominated by the giant sauropods Diplodocus, Camarasaurus, and Apatosaurus.
A large, heavily built, herbivorous quadruped, Stegosaurus had a distinctive and unusual posture, with a heavily arched back, short forelimbs, head held low to the ground and a stiffened tail held high in the air. Its array of plates and spikes has been the subject of much speculation. The spikes were most likely used for defense, while the plates have also been proposed as a defensive mechanism, as well as having display and thermoregulatory (heat control) functions. Stegosaurus was the largest of all the stegosaurians (bigger than genera such as Kentrosaurus and Huayangosaurus) and, although roughly bus-sized, it nonetheless shared many anatomical features (including the tail spines and plates) with the other stegosaurian genera.
Contents
Description
The size of a Stegosaurus compared to a human.
Averaging around 10 metres (33 ft) long and 4 metres (13 ft) tall, the quadrupedal Stegosaurus is one of the most easily identifiable dinosaurs, due to the distinctive double row of kite-shaped plates rising vertically along its arched back and the two pairs of long spikes extending horizontally near the end of its tail. Although a large animal, it was dwarfed by its contemporaries the giant sauropods. Some form of armour appears to have been necessary, as it coexisted with large predatory theropod dinosaurs, such as the fearsome Allosaurus and Ceratosaurus.
The hind feet each had three short toes, while each forefoot had five toes; only the inner two toes had a blunt hoof. All four limbs were supported by pads behind the toes. [3] The forelimbs were much shorter than the stocky hindlimbs, which resulted in an unusual posture. The tail appears to have been held well clear of the ground, while the head of Stegosaurus was positioned relatively low down, probably no higher than 1 metre (3.3 ft) above the ground. [4]
Life restoration of Stegosaurus stenops
The long and narrow skull was small in proportion to the body. It had a small antorbital fenestra, the hole between the nose and eye common to most archosaurs, including modern birds, though lost in extant crocodylians. The skull’s low position suggests that Stegosaurus may have been a browser of low-growing vegetation. This interpretation is supported by the absence of front teeth and their replacement by a horny beak or rhamphotheca. Stegosaurian teeth were small, triangular and flat wear facets show that they did grind their food. The inset placement in the jaws suggests that Stegosaurus had cheeks to keep food in their mouths while they chewed. [5]
Despite the animal’s overall size, the braincase of Stegosaurus was small, being no larger than that of a dog. A well preserved Stegosaurus braincase allowed Othniel Charles Marsh to obtain in the 1880s a cast of the brain cavity or endocast of the animal, which gave an indication of the brain size. The endocast showed that the brain was indeed very small, maybe the smallest among the dinosaurs. The fact that an animal weighing over 4.5 tonnes (5 US short tons) could have a brain of no more than 80 grams (2.8 oz) contributed to the popular old idea that dinosaurs were unintelligent, an idea now largely rejected. [6]
Most of the information known about Stegosaurus comes from the remains of mature animals; however more recently juvenile remains of Stegosaurus have been found. One sub-adult specimen, discovered in 1994 in Wyoming, is 4.6 metres (15 ft) long and 2 metres (7 ft) high, and is estimated to have weighed 2.3 tonnes (2.6 short tons) while alive. It is on display in the University of Wyoming Geological Museum. [7] Even smaller skeletons, 210 centimetres (6.9 ft) long and 80 centimetres (2.6 ft) tall at the back, are on display at the Denver Museum of Nature & Science.
Classification
Stegosaurus was the first-named genus of the family Stegosauridae. It is the type genus that gives its name to the family. Stegosauridae is one of two families within the infraorder Stegosauria, with the other being Huayangosauridae. Stegosauria lies within the Thyreophora, or armoured dinosaurs, a suborder which also includes the more diverse ankylosaurs. The stegosaurs were a clade of animals similar in appearance, posture and shape that mainly differed in their array of spikes and plates. Among the closest relatives to Stegosaurus are Wuerhosaurus from China and Kentrosaurus from east Africa.
Origins
The origin of Stegosaurus is uncertain, as few remains of basal stegosaurs and their ancestors are known. Recently, stegosaurids have been shown to be present in the lower Morrison Formation, existing several million years before the occurrence of Stegosaurus itself, with the discovery of the related Hesperosaurus from the early Kimmeridgian. [8] The earliest stegosaurid (the genus Lexovisaurus) is known from the Oxford Clay Formation of England and France, giving it an age of early to middle Callovian.
The earlier and more basal genus Huayangosaurus from the Middle Jurassic of China (some 165 million years ago) predates Stegosaurus by 20 million years and is the only genus in the family Huayangosauridae. Earlier still is Scelidosaurus, from Early Jurassic England, which lived approximately 190 million years ago. Interestingly, it possessed features of both stegosaurs and ankylosaurs. Emausaurus from Germany was another small quadruped, while Scutellosaurus from Arizona in the USA was an even earlier genus and was facultatively bipedal. These small, lightly-armoured dinosaurs were closely related to the direct ancestor of both stegosaurs and ankylosaurs. A trackway of a possible early armoured dinosaur, from around 195 million years ago, has been found in France. [9]
History
Discovery and species
Stegosaurus, one of the many dinosaurs first collected and described in the Bone Wars, was originally named by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1877, [10] from remains recovered north of Morrison, Colorado. These first bones became the holotype of Stegosaurus armatus. The basis for its scientific name, ‘roof(ed) lizard’ has been thought to have been Marsh’s initial belief that the plates lay flat over the animal’s back, overlapping like the shingles (tiles) on a roof. A wealth of Stegosaurus material was recovered over the next few years and Marsh published several papers on the genus. Initially, several species were described. However, many of these have since been considered to be invalid or synonymous with existing species, [11] leaving two well-known and one poorly-known species.
Valid species
Stegosaurus armatus, meaning «armoured roof lizard», was the first species to be found and is known from two partial skeletons, two partial skulls and at least thirty fragmentary individuals. [10] This species had four horizontal tail spikes and relatively small plates. At 10 metres (33 ft), it was the longest species within the genus Stegosaurus.
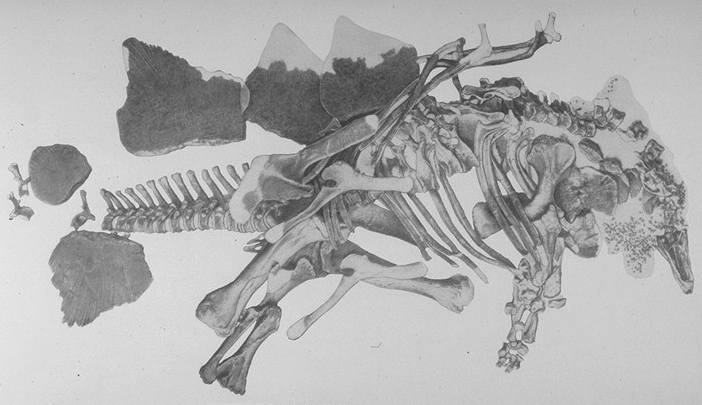
Fossil specimen of Stegosaurus stenops shown as it was found.
Stegosaurus stenops, meaning «narrow-faced roof lizard», was named by Marsh in 1887, [13] with the holotype having been collected by Marshal Felch at Garden Park, north of Cañon City, Colorado, in 1886. This is the best-known species of Stegosaurus, mainly because its remains include at least one complete articulated skeleton. It had large, broad plates and four tail spikes. Stegosaurus stenops is known from at least 50 partial skeletons of adults and juveniles, one complete skull and four partial skulls. It was shorter than S. armatus, at 7 metres (23 ft).
Stegosaurus longispinus, meaning «long-spined roof lizard», was named by Charles W. Gilmore [14] and known from one partial skeleton, from the Morrison Formation in Wyoming. Stegosaurus longispinus was notable for its set of four unusually long tail spines. Some consider it a species of Kentrosaurus. Like S. stenops, it grew to 7 metres (23 ft) in length.
Nomina dubia (dubious names)
Stegosaurus ungulatus, meaning «hoofed roof lizard», was named by Marsh in 1879, from remains recovered at Como Bluff, Wyoming. [15] It is known from a few vertebrae and armour plates. It might be a juvenile form of S. armatus, [16] although the original material of S. armatus is yet to be fully described. The specimen discovered in Portugal and dating from the upper Kimmeridgian-lower Tithonian stage has been ascribed to this species. [1]
Stegosaurus sulcatus, meaning «furrowed roof lizard» was described by Marsh in 1887 based on a partial skeleton. [13] It is considered a synonym of S. armatus. [16] Stegosaurus duplex, meaning «two plexus roof lizard» (in allusion to the greatly enlarged neural canal of the sacrum which Marsh characterized as a «posterior brain case»), is probably the same as S. armatus. [16] Although named by Marsh in 1887 (including the holotype specimen), the disarticulated bones were actually collected in 1879 by Edward Ashley at Como Bluff, Wyoming.
Stegosaurus seeleyanus, originally named Hypsirophus, is probably the same as S. armatus. Stegosaurus (Diracodon) laticeps was described by Marsh in 1881, from some jawbone fragments. [17] Just as some consider S. stenops a species of Diracodon, others consider Diracodon itself to be a species of Stegosaurus. Bakker had resurrected D. laticeps in 1986, [18] although others note that the material is non-diagnostic and likely synonymous with S. stenops. [11]
Stegosaurus affinis, described by Marsh in 1881, is only known from a pubis and is considered a nomen dubium. [16] It is possibly synonymous with S. armatus. [14]
Reassigned species
Stegosaurus madagascariensis from Madagascar is known solely from teeth and was described by Piveteau in 1926. The teeth were variously attributed to a stegosaur, the theropod Majungasaurus, [19] a hadrosaur or even a crocodylian.
Other remains originally attributed to Stegosaurus are now considered to belong to different genera. This is the case for Stegosaurus marshi, which was described by Lucas in 1901. It was renamed Hoplitosaurus in 1902. Stegosaurus priscus, described by Nopcsa in 1911, was reassigned to Lexovisaurus, [16] and is now the type species of Loricatosaurus. [20]
Paleobiology
Stegosaurus was the largest stegosaur, reaching up to 10 meters (33 ft) in length and possibly weighing up to 5,000 kilograms (5.5 short tons). However, 7 to 9 metres was a more usual length. Soon after its discovery, Marsh considered Stegosaurus to have been bipedal, due to its short forelimbs. [21] He had changed his mind however, by 1891, after considering the heavy build of the animal. [22] Although Stegosaurus is undoubtedly now considered to have been quadrupedal, there has been some discussion over whether it could have reared up on its hind legs, using its tail to form a tripod with its hind limbs and browsing for higher foliage. [16] This has been proposed by Bakker [18] [23] and opposed by Carpenter. [4]
Stegosaurus did have very short forelimbs, in relation to its hind legs. Furthermore, within the hindlimbs, the lower section (comprising the tibia and fibula) was short compared with the femur. This suggests that it couldn’t walk very fast, as the stride of the back legs at speed would have overtaken the front legs, giving a maximum speed of 6–7 kilometres per hour (4–5 mi/hr). [5]
«Second brain»
Soon after describing Stegosaurus, Marsh noted a large canal in the hip region of the spinal cord, which could have accommodated a structure up to 20 times larger than the brain. This has led to the famous idea that dinosaurs like Stegosaurus had a ‘second brain’ in the tail, which may have been responsible for controlling reflexes in the rear portion of the body. It has also been suggested that this «brain» might have given a Stegosaurus a temporary boost when it was under threat from predators. [5] More recently, it has been argued that this space (also found in sauropods) may have been the location of a glycogen body, a structure in living birds whose function is not definitely known but which is postulated to facilitate the supply of glycogen to the animal’s nervous system. [24]
Plates
The most recognizable features of Stegosaurus are its dermal plates, which consisted of 17 separate flat plates. These were highly modified osteoderms (bony-cored scales), similar to those seen in crocodiles and many lizards today. They were not directly attached to the animal’s skeleton, instead arising from the skin. In the past, some palaeontologists, notably Robert Bakker, have speculated the plates may have been mobile to some degree, although others disagree. [25] Bakker suggested that the plates were the bony cores of pointed horn-covered plates that a Stegosaurus could flip from one side to another in order to present a predator with an array of spikes and blades that would impede it from closing sufficiently to attack the Stegosaurus effectively. The plates would naturally sag to the sides of the Stegosaurus, the length of the plates reflecting the width of the animal at that point along its spine. His reasoning for these plates to be covered in horn is that the surface fossilized plates have a resemblance to the bony cores of horns in other animals known or thought to bear horns, and his reasoning for the plates to be defensive in nature is that the plates had insufficient width for them to stand erect easily in such a manner as to be useful in display without continuous muscular effort. [26] The largest plates were found over the animal’s hips and measured 60 centimetres (2 ft) wide and 60 centimetres tall. The arrangement of the plates has long been a subject of debate but most palaeontologists now agree that they formed a pair of alternating rows, one running down each side of the midline of the animal’s back.
Early reconstruction of Stegosaurus with plates lying flat along the back and tail spikes evenly distributed all over the body.
The function of the plates has been much debated. Initially thought of as some form of armour, [21] they appear to have been too fragile and ill-placed for defensive purposes, leaving the animal’s sides unprotected. [27] More recently, researchers have proposed that they may have helped to control the body temperature of the animal, [25] in a similar way to the sails of the large carnivorous Spinosaurus or of the pelycosaur Dimetrodon (and the ears of modern elephants and jackrabbits). The plates had blood vessels running through grooves and air flowing around the plates would have cooled the blood. [28] This theory has been seriously questioned, [29] since the closest relative to the common plate-wielding species, Stegosaurus stenops, had low surface area spikes instead of plates, implying that cooling was not important enough to require specialized structural formations such as plates.
Their large size suggests that the plates may have served to increase the apparent height of the animal, in order either to intimidate enemies [14] or to impress other members of the same species, in some form of sexual display, [27] although both male and female specimens seemed to have had them. A study published in 2005 supports the idea of their use in identification. Researchers believe this may be the function of other unique anatomical features, found in various dinosaur species. [30] Stegosaurus stenops also had disk-shaped plates on its hips.
One of the major subjects of books and articles about Stegosaurus is the plate arrangement. [31] The argument has been a major one in the history of dinosaur reconstruction. Four possible plate arrangements have been mooted over the years:
Thagomizer (tail spikes)
Thagomizer on mounted Stegosaurus tail.
There has been debate about whether the tail spikes were used for display only, as posited by Gilmore in 1914 [14] or used as a weapon. Robert Bakker noted the tail was likely to have been much more flexible than that of other dinosaurs, as it lacked ossified tendons, thus lending credence to the idea of the tail as a weapon. However, as Carpenter [4] has noted, the plates overlap so many tail vertebrae, that movement would be limited. Bakker also observed that Stegosaurus could have maneuvered its rear easily, by keeping its large hindlimbs stationary and pushing off with its very powerfully muscled but short forelimbs, allowing it to swivel deftly to deal with attack. [18] More recently, a study of tail spikes by McWhinney et al., [33] which showed a high incidence of trauma-related damage, confirms the spikes were indeed used in combat. Additional support for this idea was a punctured tail vertebra of Allosaurus into which a tail spike fit perfectly. [34]
Stegosaurus stenops had four dermal spikes, each about 60–90 centimetres (2–3 ft) long. Discoveries of articulated stegosaur armour show that, at least in some species, these spikes protruded horizontally from the tail, not vertically as is often depicted. Initially, Marsh described S. armatus as having eight spikes in its tail, unlike S. stenops. However, recent research re-examined this and concluded this species also had four. [11]
Stegosaurus tooth diagram.
Stegosaurus and related genera were herbivores. However, they adopted a feeding strategy different from that of the other herbivorous ornithischian dinosaurs. The other ornithischians possessed teeth capable of grinding plant material and a jaw structure capable of movements in planes other than simply orthal (i.e. they could chew plants). This contrasts with Stegosaurus (and all stegosaurians), which had small teeth having horizontal wear facets associated with tooth-food contact [35] and a jaw probably capable of only orthal movements. [16]
The stegosaurians must have been successful, as they became speciose and geographically widely distributed, in the late Jurassic. [16] Palaeontologists believe it would have eaten plants such as mosses, ferns, horsetails, cycads and conifers or fruits [36] and swallowed gastroliths to aid food processing (due to the lack of chewing ability), in the same manner used by modern birds and crocodiles. [37] Low-level browsing on grasses, seen in modern mammalian herbivores, would not have been possible for Stegosaurus, as grasses did not evolve until late into the Cretaceous Period, long after Stegosaurus had become extinct.
One hypothesised feeding behaviour strategy considers them to be low-level browsers, eating low-growing fruit of various non-flowering plants, as well as foliage. This scenario has Stegosaurus foraging at most one metre above the ground. [38] On the other hand, if Stegosaurus could have raised itself on two legs, as suggested by Bakker, then it could have browsed on vegetation and fruits quite high up, with adults being able to forage up to 6 metres (20 ft) above the ground. [5]
Behavior
Tracks discovered by Matthew Mossbrucker of the Morrison Natural History Museum from Colorado suggest that Stegosaurus lived in multi-age herds. One group of tracks is interpreted as showing four or five baby stegosaurs moving in the same direction, while another has a juvenile stegosaur track with an adult track overprinting it. [39]
Cultural Influence
Stegosaurus is among the most recognizable of dinosaurs. [5] It has been depicted in many ways; on film, in cartoons, comics, as children’s toys, and as sculpture. It even was declared the State Dinosaur of Colorado in 1982. [40] Stegosaurus is a subject for inclusion in dinosaur toy and scale model lines, such as the Carnegie Collection.
As late as the 1970s, Stegosaurus, along with other dinosaurs, was depicted in fiction as a slow-moving, dim-witted creature. The «dinosaur renaissance» changed the prevailing image of dinosaurs as sluggish and cold-blooded and this re-evaluation has been reflected in popular media. [41]
Science
In September 2002, a hoax poster was presented at the Society of Vertebrate Paleontology entitled «The case for Stegosaurus as an agile, cursorial biped», ostensibly by T. R. Karbek (an anagram of R. T. Bakker) from the non-existent «Steveville Academy of Palaeontological Studies». This was reported in New Scientist magazine, where it was remarked that Stegosaurus was generally believed to be «about as cursorial as a fridge-freezer». [42]
Literature
A sketch of a Stegosaurus forms an important plot point in the opening chapters of The Lost World by Arthur Conan Doyle. Although it is out of print (used copies are available on the Web), Evelyn Sibley Lampman wrote a children’s book about twins who find a talking Stegosaurus on their ranch; titled «The Shy Stegosaurus of Cricket Creek».
Sculpture
Sculptor Jim Gary created several, almost-life-sized versions of Stegosaurus. One always was displayed among his traveling exhibition, Jim Gary’s Twentieth Century Dinosaurs, and they are frequently used as an illustration of his work in books and articles about the artist because of their distinctive characteristics.
One displayed for months before the electrical engineering research facility at the University of North Carolina at Charlotte during a 2005 campus-wide display of the exhibition, which was hosted by Belk College, became a mascot of sorts to students studying in nearby buildings. [43]
Cinema
Over the years, Stegosaurus has seen its share of screen time, often pitted in battle against large carnivorous dinosaurs, in both theatres and television. It came up against Ceratosaurus in Journey to the Beginning of Time (1954), in The Animal World (1956), the documentary When Dinosaurs Roamed America (2001),and Jurassic Fight Club where it also faces Allosaurus (2008). It faced Allosaurus in episode two of «Walking with Dinosaurs» (1999), as well as in the special The Ballad of Big Al (2000). It was even seen pitted against Tyrannosaurus, in Planet of Dinosaurs (1978), Walt Disney’s Fantasia (1940) (which was the first time use of the spike tail for defense was portrayed), and in the remake of the series Land of the Lost (1992–93). A baby Stegosaurus dubbed Spike is one of the lead characters in The Land Before Time (1988) and its direct-to-video sequels.
In the classic monster film, King Kong (1933), the first creature that the band of rescuers meet, as they chase the abducted Fay Wray deep into Skull Island, is a roaring Stegosaurus, which charges. In the 2005 Peter Jackson remake Stegosaurus is nowhere to be seen, although in the extended edition the fictional Triceratops-like dinosaur «Ferructus» takes its place.
A Stegosaurus also has appeared in The Lost World: Jurassic Park, as one of the first dinosaurs to be seen. They also were seen briefly in Jurassic Park III. (An ailing Stegosaurus is encountered by the characters in the novel Jurassic Park, [44] but was replaced by a Triceratops in the film version.) Although it makes no actual appearance in the film, the name is used; it is on one of the embryo vials stolen (misspelled as ‘Stegasaurus’).
Stegosaurus is one of the three dinosaur species whose physical characteristics were combined by the designers at Toho, to create the Japanese monster Godzilla; the other two dinosaurs were Tyrannosaurus and Iguanodon. In the American version of King Kong vs. Godzilla this is remarked upon by a reporter, claiming Godzilla was half-Stegosaur, half-Tyrannosaur.
Cartoons and comics
Stegosaurus has been featured in children’s cartoons. The Transformers toyline and related television series features four characters which can transform into stegosaurids: Snarl, Slugfest, Saberback and Striker. In the 1980s cartoon Dinosaucers, the character Stego is an anthropomorphic Stegosaurus who while still only a trainee soldier accomplishes difficult tasks despite his inexperience. Also, Stegz was an anthropomorphic stegosaur featured in the series «Extreme Dinosaurs». Ironically, despite the tiny brain size of Stegosaurus, he is portrayed as the most intelligent of the characters in the show. One of the Dino Knights and Drago Clones in Dinozaurs were Dino Stego and his evil counterpart Drago Stegus.
Gary Larson’s The Far Side comic strip often used stegosaurs when he showed dinosaurs. The term «Thagomizer» originated as a joke from a Far Side comic strip, in which a group of cavemen in a lecture hall are taught by their caveman professor that the spikes were named in honor of «the late Thag Simmons». The implication is that the Thagomizer was responsible for Thag’s death. Whatever the original word for the spiked tail of Stegosaurus was, if it ever had one, has, since the Far Side publication, been replaced by «thagomizer», which is used as a genuine anatomical term [45] by many palaeontological authorities, including the Smithsonian Institution. [46]